In-situ chemical oxidation in dense subsoil in the inner city area, Stuttgart
- source of damage: area 375 m², depth approx. 10 m below underground car park
- 15 injection levels, GW measuring points and three soil vapor extraction levels, horizontal/sloping
- Remediation: from March 2023 (duration approx. 30 months)
Challenging site conditions
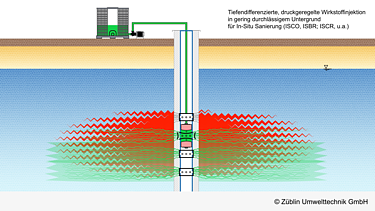
A former dry-cleaning site in the city center emits the highest CHC load of all contaminated sites in Stuttgart. Following successful laboratory and field tests, the damaged area is now being remediated using depth-differentiated, pressure-controlled injection of activated persulphate. The low permeability of the aquifer and its heterogeneous structure as well as the cramped spatial conditions in an underground car park and laundry room pose particular challenges.
Special features
- Public invitation to tender
- Laboratory/pilot test
- Join Venture with consulting company BOSSCON
- Depth-differentiated, pressure-controlled injection
- Method for activating persulfate patented
Scope of services
- Drilling work in underground garage and laundry room on 2nd floor
- Preparation/dosing station for activated persulphate
- Implementation of ISCO injection campaigns
- Creation of a hydraulic numerical flow model
- Temporary soil vapor extraction and hydraulic pollutant removal
- Monitoring